Some tasks like dynamic memory allocation, cannot be performed without using a pointer. In an earlier tutorial, we use variable name(identifier) for accessing the memory. Because the program does not need to care about the address of data it simply uses the variable_name whenever it needs to refer to the variable_value.But when we are working with heap memory(dynamic memory) we need to remember the address of data. I think you are a little bit confuse about memory?
The computer memory is a collection of storage cells.Each cell, commonly known as byte,has a large number called address associated with it.
Whenever, we declare a variable the computer allocates, somewhere in the memory, an appropriate location to hold the value of the variable this location will have its own unique address. For example:-

During the execution of the program, the system always associates the value with the address.
We may have access to 10 by using either value or address.Since addresses are numbers that can be also stored like other variables.Such variable that holds memory address is known as Pointer
A pointer is a derived data type in C. It contains the memory addresses as their value. It can be used to access and manipulate data stored in the memory. Like any variable or constant, you must declare a pointer before using it to store any variable address. A general form of a pointer is −
data_type tells that the ptr-name contains the address of data_type variable.
Initialization of pointer variable
Once a pointer variable has been declared we can use the assignment operator to initialize the variable.A general form is:-
C Code Example
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
#include <stdio.h> void main() { int value =10; int *ptr =&value; printf("value = %d address =%d",value,ptr); } |

Note:-Pointer should be initialized other it store any garbage value.
A pointer can be initialized with NULL or zero value.
Pointer to Pointer
It is possible to make a pointer to point another pointer. The syntax simply requires an dereference operator(*) for each level of indirection in the declaration of the pointer:
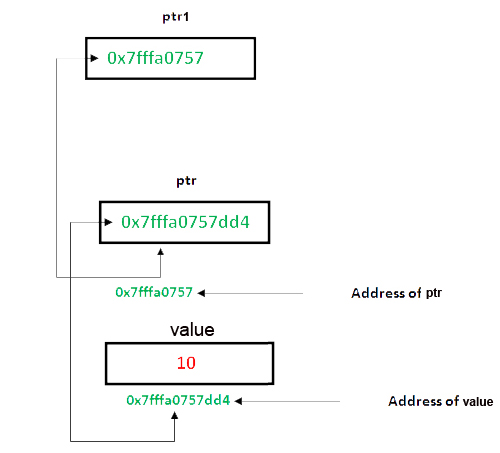
C Code Example
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
#include <stdio.h> void main() { int value =10; int *ptr = &value; int **ptr2 = &ptr; printf("value = %d address =%d",value,ptr); printf("\naddress of ptr =%d",ptr2); } |